Windows Task Manager
How to Open the Windows Task Manager
Like most things in Windows, there are several ways to open the Task Manager. I’ll show you the shortcuts, here are five ways.
- Press the keys Ctrl+Shift+Esc at the same time.
- Press the keys Ctrl+Alt+Del at the same time. This will bring up a menu where you can click on Task Manager.
- Press the keys Win+X to bring up the Quick Link menu, then select Task Manager.
- Right-click on an empty area of your Taskbar, then select Task Manager
- From the Start menu, type “Task Manager“, as you start typing it will show up in the list. Select it to open it.
What does the Task Manager tell you?
The first time opening the Task Manager, it doesn’t look there is much to talk about, but there’s a lot more to see.
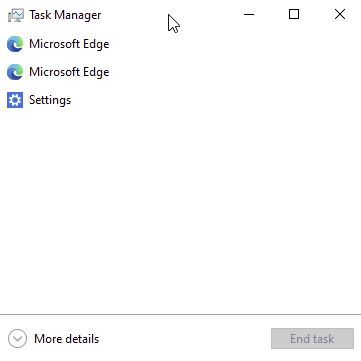
Click on “More details” in the bottom left. This will show you an advanced view of the Task Manager. There are tabs across the top that show you different aspects of what is running.
Processes
This is where you can easily see which processes are using resources. You can sort by clicking on the top headers (CPU, Memory, Disk, Network, Power), which toggle from High to Low. You can right-click on any process to bring up a menu from which you can see more details and to “End task”.
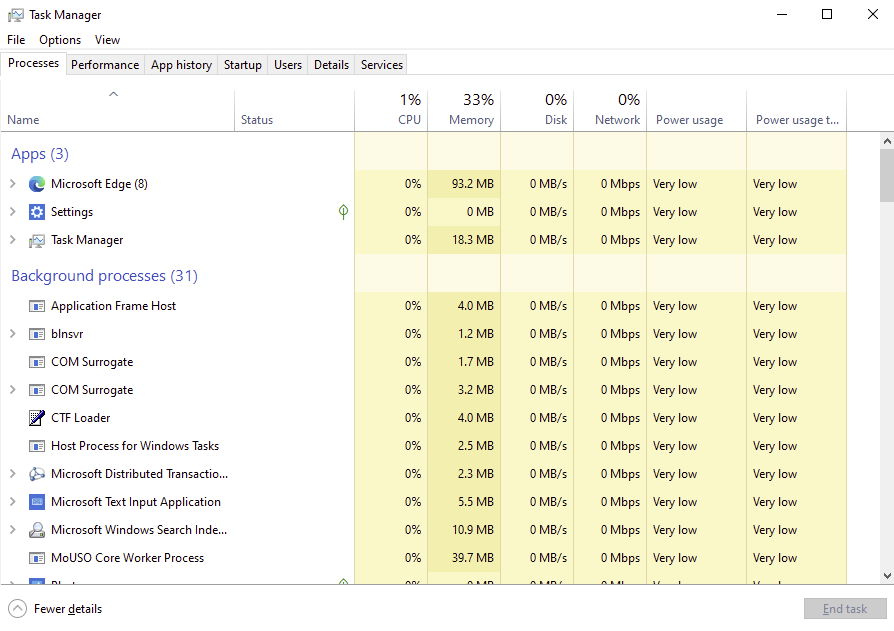
Performance
The performance tab lets you see a graph of some of the key resources. CPU, Memory, Disk, Network.
App history
Under App history, it shows you some details on Microsoft Store Apps that are running.
Startup
The Startup list applications that are configured to possibly start when your computer starts. You can right-click on an item and change the status between Enabled & Disabled.
Users
This view shows the processing running grouped by users. In the example below there is only one user “admin” and it shows what is running under that user.
Details
Details show all processes running by any user or any system process. This view is my preferred tab to view what and who (user) is using CPU & Memory.
Services
These are mostly processes that are part of Windows. As you install programs, they may add their own service to this list. Mostly you shouldn’t change anything here unless you know what you are doing.
Common Problems
Two of the most common issues you may see when looking at running processes are disk usage at 100% and a process showing “Not responding”. This can be an indicator of problems like some filesystem corruption or a crashed application. If you’ve waited a reasonable about of time, maybe 5-10 minutes, then I would just reboot the computer.
You can also see similar issues when your computer is installing Windows updates. It’s best to let the updates complete before rebooting.
You should now know a lot more about the Task Manager
Hope this helped you better understand what the Task Manager is and the things you can see with it. There also another tool you can run called Process Explorer. This is part of the Windows Sysinternals utilities.